CCNP Service Provider SPRI – Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions

The SPRI Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions course is part of the Cisco CCNP Service Provider track . This course focuses on advanced routing topics, addressing the following topics: OSPF Multiarea, IS-IS Multilevel, Routing Policy Language, Route Redistribution, BGP Route Selection, MPLS Traffic Engineering, Segment Routing, IPv6 Tunneling Mechanisms, Multicast, PIM-SM, Rendezvous Point Distribution, and more. The course contributes to the preparation of the CCNP Service Provider Certification exam (Exam 300-510) .
Course Objectives
The following is a summary of the main objectives of the SPRI Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions Course :
- Understand and apply OSPF Multiarea and IS-IS Multilevel.
- Familiarize yourself with Routing Policy Language and Route Redistribution.
- Approfondire BGP Route Selection e MPLS Traffic Engineering.
- Gain skills on Segment Routing and IPv6 Tunneling Mechanisms.
- Studiare Multicast, PIM-SM e Rendezvous Point Distribution.
- Develop expertise in advanced BGP features, including BGP EVPN and route reflectors.
- Master MPLS Layer 3 VPN and MPLS Layer 2 VPN technologies.
- Explore best practices for network design and optimization in service provider environments.
Course Certification
This course helps you prepare to take the:
Exam 300-510 SPRI Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions;
Course Outline
- Unicast Routing
- Compare OSPF and IS-IS routing protocols
- Troubleshoot OSPF multiarea operations (IPv4 and IPv6)
- Route advertisement
- Summarization
- Troubleshoot IS-IS multilevel operations (IPv4 and IPv6)
- Route advertisement
- Summarization
- Describe the BGP scalability and performance
- BGP confederations
- Route reflectors
- Troubleshoot BGP
- Route advertisement
- Route reflectors
- Confederations
- Multihoming
- TTL security and inter-domain security
- Maximum prefix
- Route dampening
- Dynamic neighbors
- Communities
- Describe IPv6 tunneling mechanisms
- Static IPv6-in-IPv4 tunnels
- Dynamic 6to4 tunnels
- IPv6 provider edge (6PE)
- Implement fast convergence
- Bidirectional forwarding detection
- Nonstop Forwarding
- NSR
- Timers
- BGP pic (edge and core)
- LFA
- BGP additional and backup path
- Multicast Routing
- Compare multicast concepts
- Multicast domains, distribution trees, and IGMP operations
- Any-Source Multicast (ASM) versus Source Specific Multicast (SSM)
- Intra-domain versus inter-domain multicast routing
- Describe multicast concepts
- Mapping of multicast IP addresses to MAC addresses
- Multiprotocol BGP for IPv4 and IPv6
- Principles and operations of PIM-SM
- Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) operations
- MLDP/P2MP
- Implement PIM-SM operations
- Auto-RP, PIMv2 BSR, anycast RP
- BIDIR-PIM operations
- SSM operations
- MSDP operations
- Troubleshoot multicast routing
- Single domain
- Multidomain
- Routing Policy and Manipulation
- Compare routing policy language and route maps
- Describe conditional matching
- Operations
- Semantics of policy applications and statements
- Regular expressions
- Policy sets
- Tags
- ACLs
- Prefix lists and prefix sets
- Route types
- BGP attributes and communities
- Hierarchical and parameterized structures
- Troubleshoot route manipulation for IGPs
- IS-IS
- OSPF
- Troubleshoot route manipulation for BGP
- Route filtering
- Traffic steering
- MPLS and Segment Routing
- Troubleshoot MPLS
- LDP
- LSP
- Unified BGP
- BGP free core
- RSVP TE tunnels
- Implement segment routing
- Routing protocol extensions (OSPF, IS-IS, BGP)
- SRGB and SRLB
- Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA)
- Migration procedures (SR prefer and mapping server)
- Describe segment routing traffic engineering
- Automated steering and coloring
- Policies (constraints, metrics, and attributes)
- PCE-based path calculation
- Describe segment routing v6 (SRv6)
- Control plane operations
- Data plane operations
Laboratory Activities
- Implement OSPF Special Area Types (IPv4 and IPv6)
- Implement Multiarea IS-IS
- Implement Route Redistribution
- Influence BGP Route Selection
- Implement BGP Route Reflectors
- Implement BGP Security Options
- Troubleshoot Routing Protocols
- Implement MPLS in the Service Provider Core
- Implement Cisco MPLS TE
- Configure and Verify Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) Segment Routing
- Implement Tunnels for IPv6
- Enable and Optimize PIM-SM
- Implement PIM-SM Enhancements
- Implement Rendezvous Point Distribution
Course Mode
Instructor-Led Remote Live Classroom Training;
Trainers
Trainers are Cisco Official Instructors and certified in other IT technologies, with years of hands-on experience in the industry and in Training.
Lab Topology
For all types of delivery, the Trainee can access real Cisco equipment and systems in our laboratories or directly at the Cisco data centers remotely 24 hours a day. Each participant has access to implement the various configurations thus having a practical and immediate feedback of the theoretical concepts.
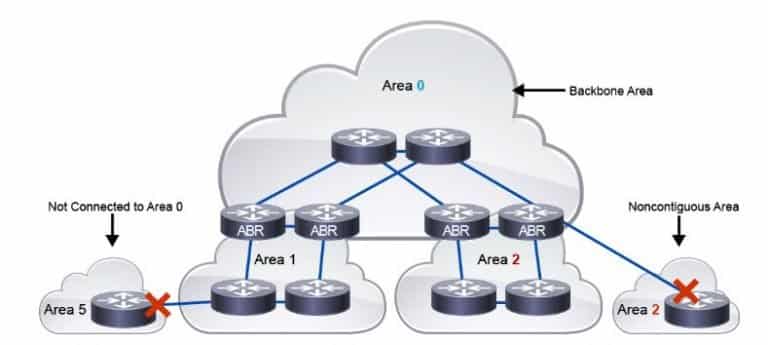
Here are some Cisco Labs network topologies available:
Course Details
Course Prerequisites
Attendance at the Cisco CCNA Course is recommended .
Course Duration
Intensive duration 5 days
Course Frequency
Course Duration: 5 days (9.00 to 17.00) - Ask for other types of attendance.
Course Date
- Cisco SPRI Course (Intensive Formula) – On request – 9:00 – 17:00
Steps to Enroll
Registration takes place by asking to be contacted from the following link, or by contacting the office at the international number +355 45 301 313 or by sending a request to the email info@hadartraining.com


